Training session at LISIS and Wikiversity tutorials
On the 20th of January, the Cortext team organized a full day workshop on quali-computational analysis of textual corpora at the Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire Sciences Innovations Sociétés [...]
At Cortext, our goal is to empower researchers by promoting advanced qualitative-quantitative mixed methods. Our primary focus is on studies about the dynamics of science, technology and innovation, and about the roles of knowledge and expertise in societies.
We understand the move towards digital humanities and computational methods not as addressing a technological gap for the social sciences, but rather as entailing entirely new assemblages between its disciplines and those of modern statistics and computer sciences. And we work to tackle ever more complex research problems and deal with the profusion of new and diverse sources of information without losing sight of the situatedness and reflexivity required of studies of human societies.
Cortext is hosted by the LISIS research unit at Gustave Eiffel University, and was launched by French institutes IFRIS and INRAE, receiving their continued support.
On the 20th of January, the Cortext team organized a full day workshop on quali-computational analysis of textual corpora at the Laboratoire Interdisciplinaire Sciences Innovations Sociétés [...]
Our team was very pleased to receive the visit of Paulo Meirelles, associate professor at the department of Computer Science of the University of São Paulo (USP), who joined us between the 12th [...]
On the 5th, 6th and 7th of November we co-organized and participated in the ANF Corpus Istex, a National Training Action led by the Istex infrastructure of the French National Institute for [...]
Invited by the Bureau d’Analyses Macro Économiques (BAME) in Dakar, Senegal, we and twenty participants examined and analyzed the research conducted since 2001 on the subject of climate [...]
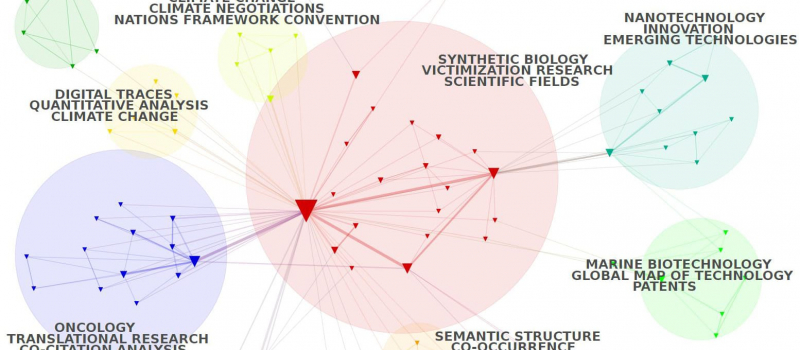
 Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.
Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.
Upload a textual corpus in order to analyse its discourse, names, categories, citations, places, dates etc, with methods for science/controversy/issue mapping, distant reading, document clustering, geo-spatial and network visualizations, and more.
You can jump straight to Cortext Manager and create an account, but we suggest taking a look at the Documentation and Tutorials as you start your journey.
Richards, Christina L; Ervens, Barbara; Parmesan, Camille; Amato, Pierre; Andrade, Christhel; Asatryan, Gayane; Balaji, Venkatramani; Ballantyne, Ashley; Barbier, Marc; Blanc, Stéphane; Bossdorf, Oliver; Bouchard, Frédéric; Boucharel, Julien; Cantrell, Christopher; Capron, Emilie; Carbonne, Chloe; Carrier, Marion; Ceratti, Davide; Choi, Heechae; Christoforodis, Konstantinos; Clark, James; Cojocaru, Ludmila; Derry, Louis; Dewar, William; Dubo, Titouan; Espinoza, Jhan-Carlo; Fedorov, Alexey; Forte, Alessandro; Giambastiani, Giuliano; Giannini, Alessandra; Goldthau, Andreas; González-García, Alberto; Guemas, Virginie; Hamelin, Lorie; Hill, Eric; Hoveyda, Amir; Hughes-Allan, Lara; Jatav, Sanjay; Javourez, Ugo; Kaplan, Jed; Keppetipola, Nilanka; Kiko, Rainer; Lauvaux, Thomas; Lazarus, David; Lee, Carol Eunmi; Lguensat, Redouane; Lucas-Picher, Philippe; Mallick, Monalisa; da Costa, Joenio Marques; Melnikova, Irina; Monnain, Guillaume; Özen, Volkan; Palomo, Ignacio; Parepa, Madalin; Possner, Anna; Renard, Delphine; Ridde, Valery; Rivada-Wheelaghan, Orestes; de Faria, Gabrielle Rodrigues; Sanderson, Benjamin; Scheer, Clemens; Schulz, Philip; Strutz, Stavana; Subramanian, R; Tanaka, Katsumasa; Teixidó, Núria; Tesche, Matthias; Thomas, Helmuth; Todorović, Sara; Tsai, Yutsung; Turnheim, Bruno; Uchida, Takaya; Vadez, Vincent; Valla, Pierre; van Riemsdijk, Isolde; Villard, Lionel; Vincent, Emmanuel; Wang, Chien; Wu, Henry; Zuerch, Michael
Multidisciplinary science funding is more than ever a planetary priority: Reflections from the Make Our Planet Great Again (MOPGA) program Journal Article
In: PLOS Climate, 2026.
@article{Richards2026,
title = {Multidisciplinary science funding is more than ever a planetary priority: Reflections from the Make Our Planet Great Again (MOPGA) program},
author = {Christina L Richards and Barbara Ervens and Camille Parmesan and Pierre Amato and Christhel Andrade and Gayane Asatryan and Venkatramani Balaji and Ashley Ballantyne and Marc Barbier and Stéphane Blanc and Oliver Bossdorf and Frédéric Bouchard and Julien Boucharel and Christopher Cantrell and Emilie Capron and Chloe Carbonne and Marion Carrier and Davide Ceratti and Heechae Choi and Konstantinos Christoforodis and James Clark and Ludmila Cojocaru and Louis Derry and William Dewar and Titouan Dubo and Jhan-Carlo Espinoza and Alexey Fedorov and Alessandro Forte and Giuliano Giambastiani and Alessandra Giannini and Andreas Goldthau and Alberto González-García and Virginie Guemas and Lorie Hamelin and Eric Hill and Amir Hoveyda and Lara Hughes-Allan and Sanjay Jatav and Ugo Javourez and Jed Kaplan and Nilanka Keppetipola and Rainer Kiko and Thomas Lauvaux and David Lazarus and Carol Eunmi Lee and Redouane Lguensat and Philippe Lucas-Picher and Monalisa Mallick and Joenio Marques da Costa and Irina Melnikova and Guillaume Monnain and Volkan Özen and Ignacio Palomo and Madalin Parepa and Anna Possner and Delphine Renard and Valery Ridde and Orestes Rivada-Wheelaghan and Gabrielle Rodrigues de Faria and Benjamin Sanderson and Clemens Scheer and Philip Schulz and Stavana Strutz and R Subramanian and Katsumasa Tanaka and Núria Teixidó and Matthias Tesche and Helmuth Thomas and Sara Todorović and Yutsung Tsai and Bruno Turnheim and Takaya Uchida and Vincent Vadez and Pierre Valla and Isolde van Riemsdijk and Lionel Villard and Emmanuel Vincent and Chien Wang and Henry Wu and Michael Zuerch},
url = {https://journals.plos.org/climate/article?id=10.1371/journal.pclm.0000849},
doi = {/10.1371/journal.pclm.0000849},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-03-11},
journal = {PLOS Climate},
abstract = {Global change poses “wicked problems” that have become ever more complex, pervasive, and damaging. Developing innovative solutions increasingly require diverse research approaches. The Franco-German Make Our Planet Great Again (MOPGA) program was designed to create a unique international network of top-level research, from fundamental to solution-oriented projects. MOPGA stands out from other large research initiatives by focusing not on a singular central research challenge but on facilitating multidisciplinary interactions between traditionally separated fields. MOPGA recognized that social, natural and engineering sciences share a unifying aim to address global change. In addition to addressing timely and innovative research questions within disciplines, MOPGA worked to improve communication across disciplines via annual meetings for all laureates and their research groups, scientific board exchanges, and public online seminars. Drawing on our MOPGA experiences, we discuss how such exchanges should be extended to meet the needs identified by the scientific community, international policy-makers, and regional stakeholders. In the current political landscape of scientific suppression and heightened mistrust in scientific expertise, the need for such bold, independent and collaborative scientific initiatives is greater than ever.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
van Wyk, Angus John; Stuart-Smith, Rick D.; Goetze, Jordan S.; Maire, Eva; Heyns-Veale, Elodie; Smit, Kaylee; Langlois, Tim J.; MacNeil, M. Aaron; Matus, Alejandro Perez; Lombard, Amanda T.; Carolina, Ana; Semmens, Christy; Clausius, Ella; Rolim, Fernanda A.; Lefcheck, Jonathan S.; Monk, Jacquomo; Schmid, Joanna K.; Tattersall, Katherine; Ghigliotti, Laura; Adams, Luther; Samoilys, Melita; Chabanet, Pascale; Whomersley, Paul; Walsh, Peter; Masuda, Reiji; Brainard, Russell; Bernard, Anthony
Global Analysis of Shallow Underwater Fish Observation Research: 70 Years of Progress, Persistent Geographic Biases and a Path Forward Journal Article
In: Fish and Fisheries, 2026.
@article{vanWyk2026,
title = {Global Analysis of Shallow Underwater Fish Observation Research: 70 Years of Progress, Persistent Geographic Biases and a Path Forward},
author = {Angus John van Wyk and Rick D. Stuart-Smith and Jordan S. Goetze and Eva Maire and Elodie Heyns-Veale and Kaylee Smit and Tim J. Langlois and M. Aaron MacNeil and Alejandro Perez Matus and Amanda T. Lombard and Ana Carolina and Christy Semmens and Ella Clausius and Fernanda A. Rolim and Jonathan S. Lefcheck and Jacquomo Monk and Joanna K. Schmid and Katherine Tattersall and Laura Ghigliotti and Luther Adams and Melita Samoilys and Pascale Chabanet and Paul Whomersley and Peter Walsh and Reiji Masuda and Russell Brainard and Anthony Bernard},
url = {https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/faf.70072
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1111/faf.70072},
doi = {/10.1111/faf.70072},
year = {2026},
date = {2026-02-15},
urldate = {2026-02-15},
journal = {Fish and Fisheries},
abstract = {Marine ecosystems are increasingly threatened by overfishing, pollution, coastal development and climate change, underscoring the need for long-term, representative information on key fish populations and habitats to inform management and policy. Underwater fish observation (UFObs) techniques, such as Underwater Visual Census (UVC), stereo-Baited Remote Underwater Video (stereo-BRUV) and Remotely Operated Vehicles (ROVs), play a key role in sustaining long-term data collection. Despite technological advancements, gaps persist in understanding research focus, geographic distribution and methodological biases inherent in these methods. We conducted a scientometric analysis of 1443 peer-reviewed publications (1953–2023), employing natural language processing and network analysis to map the research landscape. We identified 15 knowledge clusters, including marine protected areas, apex predator conservation and reef ecosystems. Our findings reveal increasing use of BRUVS and ROVs in studies of marine protected areas and subsea infrastructure, while UVC remains prevalent in shallow coral reef research. Geographic representation is skewed, with the field dominated by researchers based in Australia and the United States, and underrepresented in Africa and Southeast Asia. This imbalance highlights the need for more inclusive, globally coordinated monitoring and reporting. Our results underscore the urgency of standardising protocols within each observation method and developing interoperable reporting frameworks across techniques to maximise data comparability and foster international collaboration. Addressing these challenges will strengthen the field's capacity to inform global conservation strategies and support sustainable fisheries management.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Raimbault, Benjamin
Calculer les impacts environnementaux des activités industrielles - Surmonter les frictions et la critique par la science Journal Article
In: Statistique et société, 2025.
@article{Raimbault2025,
title = {Calculer les impacts environnementaux des activités industrielles - Surmonter les frictions et la critique par la science},
author = {Benjamin Raimbault},
url = {https://journals.openedition.org/statsoc/4199
https://journals.openedition.org/statsoc/pdf/4199},
doi = {/10.4000/15fd2},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-12-22},
journal = {Statistique et société},
abstract = {Cet article décrit comment des représentant·es d’une agence publique parviennent à produire un impact environnemental chiffré de produits de grande consommation à partir de méthodes d’Analyse de cycle de vie (ACV) développées initialement par et pour l’industrie. Ces méthodes font l’objet de controverse lorsqu’elles équipent un instrument d’action publique. Nous montrons que ces agents publics s’appuient sur la complexité et la scientificité des méthodes ACV pour surmonter les nombreuses frictions liées à l’hétérogénéité du contexte de production et aux contestations soulevées lorsque ces méthodes sont utilisées pour développer un affichage environnemental des produits alimentaires. Le travail de démarcation mené permet conjointement de remobiliser les acteur·ices des filières agricoles dans la production de calculs (remontée de données, accord sur les conventions de calcul) tout en transformant les critiques en ressources pour perfectionner les méthodes. Notre propos se fonde sur une enquête au long cours menée au sein d’un Groupement d’intérêt scientifique entre 2021 et aujourd’hui, incluant 19 entretiens avec les membres du groupe et l’observation d’une vingtaine de réunions.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Víquez, Sofia Guevara; Kotras, Baptiste
Urban politics of ordinary digital participation - From risk management to environmental mobilization in San José, Costa Rica Journal Article
In: Open edition journals, vol. 39-1/2, 2025.
@article{Víquez2025,
title = {Urban politics of ordinary digital participation - From risk management to environmental mobilization in San José, Costa Rica},
author = {Sofia Guevara Víquez and Baptiste Kotras},
url = {https://journals.openedition.org/netcom/9839},
doi = {/10.4000/1572p},
year = {2025},
date = {2025-11-29},
journal = {Open edition journals},
volume = {39-1/2},
abstract = {Based on long-term ethnographic and “chatnographic” fieldwork (2015-2024), this article examines the ordinary uses of digital technologies in urban risk management in San José, Costa Rica, focusing on residents’ communication practices via WhatsApp and Facebook around flooding of the Ocloro River. It analyzes how inhabitants mobilize mainstream digital tools to organize collectively in the face of environmental risks and to redefine their relationship with territory and public institutions. Our paper combines interviews, participant observation, and qualitative and quantitative analysis of 4,479 messages exchanged in a WhatsApp group created and managed by residents. The results highlight three main dynamics: (1) the infrapolitical self-organization of residents during emergencies; (2) the accountability—and at times contestation—of public authorities, made possible through the circulation of images, data, and digital traces; and (3) the gradual politicization of environmental issues, leading to collective mobilization for the protection of the river basin, beyond the immediate concern of flooding.
The study thus reveals a process of digital placemaking, in which social media become instruments for producing knowledge and governing territory “from below.” WhatsApp and Facebook—everyday, mainstream applications—are used for the production, archiving, and mobilization of lay knowledge in legal and political action. In the Latin American context, these ordinary digital practices contribute to reconfiguring urban governance and transforming citizen participation into a locally grounded form of environmental action.
===========
Politiser l'espace urbain par la participation numérique ordinaire De la gestion de risque à la mobilisation environnementale à San José, Costa Rica
Fondé sur une enquête ethnographique et « chatnographique » de long terme (2015-2024), cet article examine les usages ordinaires des technologies numériques dans la gestion des risques urbains à San José (Costa Rica), en se concentrant sur les pratiques de communication via WhatsApp et Facebook des habitant·es, autour des inondations du fleuve Ocloro. Il analyse la manière dont les habitants mobilisent des outils numériques grand public pour s’organiser face aux risques environnementaux et redéfinir leurs rapports au territoire et aux institutions. L’article combine entretiens, observations participantes et analyse qualitative et quantitative de 4 479 messages échangés sur un groupe WhatsApp créé et animé par les habitant·es. Les résultats montrent que ces usages numériques soutiennent trois dynamiques principales : (1) une auto-organisation infra-politique des habitants face aux urgences ; (2) une mise en responsabilité voire une contestation des autorités publiques, rendue possible par la circulation d’images, de données et de traces numériques ; (3) une politisation progressive des enjeux environnementaux, donnant lieu à une mobilisation collective pour la protection du bassin versant, au-delà du seul risque d’inondation. L’étude met ainsi en évidence un processus de digital placemaking, où les médias sociaux deviennent des instruments de connaissance et de gouvernement du territoire « par le bas ». WhatsApp et Facebook, applications grand public et utilisées au quotidien, sont mobilisées pour la production de savoirs profanes sur les risques, leur archivage et leur mobilisation dans des actions juridiques et politiques. Dans le contexte latino-américain, ces pratiques ordinaires du numérique contribuent à reconfigurer la gouvernance urbaine et à transformer la participation citoyenne en une forme d’action environnementale localement située.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Want to stay up-to-date with the latest training sessions and developments in our methods and data? We invite you to subscribe to Cortext Newsfeed, our succint and researcher oriented quarterly newsletter.
Read the previous editions of our newsletter
Cortext is supported by LabEx SITES