Cortext Manager
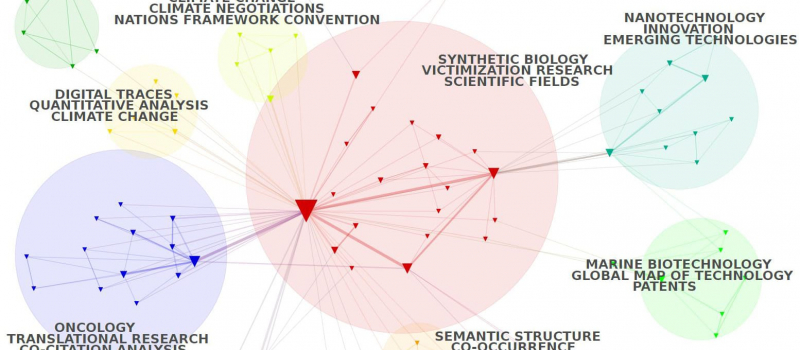
 Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.
Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.
Upload a textual corpus in order to analyse its discourse, names, categories, citations, places, dates etc, with methods for science/controversy/issue mapping, distant reading, document clustering, geo-spatial and network visualizations, and more.
You can jump straight to Cortext Manager and create an account, but we suggest taking a look at the Documentation and Tutorials as you start your journey.

 Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.
Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.