@article{Li2024,
title = {Computational intelligence and its dynamic development: statistical exploration, comprehensive evaluation and prospect expansion},
author = {Bo Li and Zeshui Xu and Xinxin Wang},
url = {https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00500-024-09789-7},
doi = {/10.1007/s00500-024-09789-7},
year = {2024},
date = {2024-07-05},
journal = {Soft Computing},
volume = {28},
pages = {9371–9386},
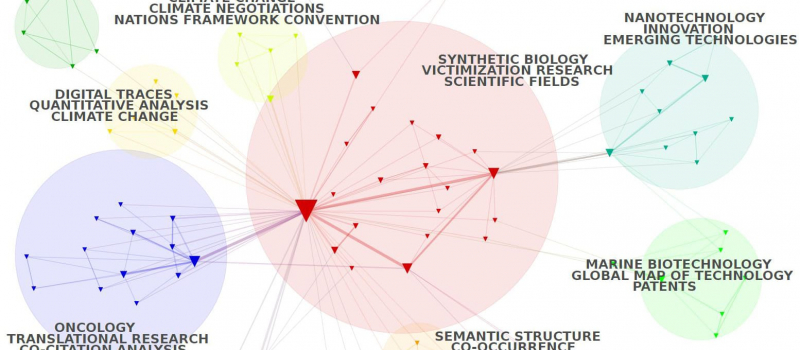
abstract = {Computational intelligence (CI) has become one of the most useful and successful tools for dealing with uncertainties and complex problems in many fields, such as neural networks, genetic algorithms, and swarm intelligence, artificial intelligence, risk management, financial monitoring, etc. With the development of CI, abundant publications have arisen related to many research directions and hotspots. Based on the technical support from bibliometrics and the corresponding approach as well as the content analysis, this study conducts a science mapping analysis and a coherent knowledge picture of the research field in CI. The research contributes to clear future development trends and provides more ideas for scholars in this field. First, this paper focuses on the fundamental characteristics of CI publications, including annual numbers, term co-occurrence, and hot research directions, as the preliminary exploration of this field. Then, according to the widely used core database, i.e., Web of Science (WoS), and the technologies of software, VOS viewer, and CiteSpace, the productive institutions, authors, and journals are explored. Next, the corresponding internal characteristics of the CI research are analyzed, including the citation features of countries/regions, institutions, journals and authors. Furthermore, to analyze the development trend of research hotspots, the keywords of all CI publications are studied: (a) classifying them into three phases in chronological order aimed; (b) implementing the burst detection algorithm to intuitively reflect the scientific research in the field of CI. Finally, this paper provides a relatively throughout perspective for the CI articles and reviews and discloses the future development trend, which will help the scholars interested in this area conduct deep research. We conclude this bibliometric overview with the limitations and recommendations for future research in the field of CI.},
keywords = {},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}

 Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.
Cortext Manager is our current main attraction, a publicly available web application providing data analysis methods curated and developed by our team of researchers and engineers.